About University of Cambridge
University of Cambridge
Articles by University of Cambridge
Angiotensin II type 1 receptor and the activation of Myosin Light-Chain Kinase and Protein Kinase C-βII: Mini Review
Published on: 17th February, 2020
OCLC Number/Unique Identifier: 8534733539
The involvement of the angiotensin II type 1 receptor in the Frank-Starling Law of the Heart, where the various activations are very limited, allows simple analysis of the kinase systems involved and thence extrapolation of the mechanism to that of angiotensin control of activation of cardiac and skeletal muscle contraction. The involvement of phosphorylation of the myosin light chain in the control of contraction is accepted but not fully understood. The involvement of troponin-I phosphorylation is also indicated but of unknown mechanism. There is no known signal for activation of myosin light chain kinase or Protein Kinase C-βII other than Ca2+/calmodulin but the former is constitutively active and thus has to be under control of a regulated inhibitor, the latter kinase may also be the same. Ca2+/calmodulin is not activated in Frank-Starling, i.e. there are no diastolic or systolic [Ca2+] changes. I suggest here that the regulated inhibition is by myosin light chain phosphatase and/or β-arrestin. Angiotensin activation, not involving G proteins. is by translocation of the β-arrestin from the sarcoplasm to the plasma membrane thus reducing its kinase inhibition action in the sarcoplasm. This reduced inhibition has been wrongly attributed to a mythical downstream agonist property of β-arrestin.
The mechanisms of cardiac myopathies, a kinetics approach: Leading review
Published on: 16th July, 2020
OCLC Number/Unique Identifier: 8631130997
The normal adult heart is a well maintained machine that has a mechanism for growth replacement of the sarcomere that is lost by natural degeneration. This process ensures the heart has the strength of contraction to function correctly giving blood supply to the whole body. Some of the force of contraction of the sarcomere is transmitted to its major protein titin where its strength results in unfolding of a flexible section and release of a growth stimulant. The origin of all the cardiomyopathies can be traced to errors in this system resulting from mutations in a wide variety of the sarcomeric proteins. Too much or chronic tension transfer to titin giving increased growth resulting in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) and too little leading to muscle wastage, dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM). HCM can ultimately lead to sudden cardiac death and DCM to heart failure. In this paper I show (1) a collection of the tension/ATPase calcium dependencies of cardiac myofibrils that define the mechanism of Ca2+ cooperativity. (2) I then reintroduce the stress/strain relationship to cardiomyopathies. (3) I then review the cardiomyopathy literature that contains similar Ca2+ dependency data to throw light on the mechanisms involved in generation of the types of myopathies from the mutations involved. In the review of cardiomyopathy there are two sections on mutations, the first dealing with those disrupting the Ca2+ cooperativity, i.e. the Hill coefficient of activation, leading to incomplete relaxation in diastole, chronic tension, and increased growth. Secondly dealing with those where the Ca2+ cooperativity is not affected giving either increased or decreased tension transfer to titin and changes in sarcomere growth.
New insights from cardiac muscle applied to skeletal muscle
Published on: 15th January, 2021
OCLC Number/Unique Identifier: 8897946095
I have recently described the origin of the second Ca2+ binding in the triggering of contractile activity in cardiac myofibrils that is the origin of the Ca2+ Hill coefficient of 2 for the ATPase. This site is not a simple protein binding site and cannot be measured by 45Ca2+ binding. The myofibril protein unit requirements are described by me and so are the consequences of disruption of the function of these units and the related medical outcomes. The purpose of this paper is to review the topic and extend the reasoning to the function of skeletal muscle and cite the literature that supports this.
Muscle growth and control of production of sarcomere components
Published on: 12th March, 2021
OCLC Number/Unique Identifier: 8958448210
Here I contrast the skeletal and cardiac muscle in terms of the control muscle growth and of sarcomere component synthesis. The differences are major and reflect the long term needs of the two systems. With the skeletal system there is growth of both the number of myocytes and the sarcomere components within them dependent on demand made of the muscle. Unlike skeletal muscles the normal adult heart is greatly restricted in size, number of myocytes and their content of contractile proteins, i.e. there is little change on demand. Over time proteins get damaged or decay and for the normal heart this implies a strictly controlled maintenance synthesis of sarcomere components. From the studies of abnormal, mutated systems there is one thing inherent to and more pronounced in cardiac muscle, the FrankStarling Law of the Heart derived from the angiotensin ii type 1 receptor that my studies indicate is central to the control of sarcomere component synthesis.
Ocular surface Rose Bengal staining in normal dogs and dogs with Keratoconjunctivitis Sicca: Preliminary findings
Published on: 30th October, 2017
OCLC Number/Unique Identifier: 7325075478
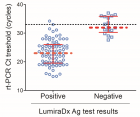
Dry eye or keratoconjunctivitis sicca, is commonly seen in the dog. Veterinary ophthalmologists diagnose this aqueous tear deficiency using the Schirmer tear test (STT), but this measures tear production and does not indicate ocular surface pathology. The vital dye Rose Bengal is commonly used in the diagnosis of dry eye in human patients but until now has not been reported in veterinary patients. Here we corelate the degree of Rose Bengal staining with the STT value and find a reasonable association between dye staining of the ocular surface and tear production, although clearly other factors are also important in the genesis of ocular surface damage in dry eye.
The Outcome of an ADHD Parenting Group Training Programme (APEG) In the Peterborough Neurodevelopmental Service (NDS)
Published on: 27th January, 2017
OCLC Number/Unique Identifier: 7317597712
ADHD is the most common neurodevelopmental disorder in children and adolescents with prevalence ranging between 5% and 12% in developed countries. There is ample evidence that carefully structured enhanced behavioural parenting programmes are useful in the management of ADHD.
We assessed the outcome of an ADHD group parenting training programme (APEG) offered between 2014 and 2015 by the Peterborough Neurodevelopmental Service (NDS) in improving the knowledge and skills of carers using a pre-/post-training intervention study.
APEG follows a Parent Advisor Model, consisting of a 6-session programme of evidence-based parenting training.
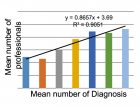
A total of 27 parents completed the 53 pre- and post-course questionnaires. The knowledge and understanding of the parents increased significantly about all aspects of ADHD diagnosis and management in response to all the 5 questions. The difference between the scores of 0 to 3 and 4 or 5 pre- and post-intervention was statistically significant (chi square 239, df 1, p value <0.01).
The study suggests that provision of a psychosocial intervention programme for parents of ADHD children through the APEG parenting training proved to be effective in significantly improving the level of knowledge and understanding of parents regarding several aspects of ADHD diagnosis, symptom identification and behaviour control.

If you are already a member of our network and need to keep track of any developments regarding a question you have already submitted, click "take me to my Query."